Ten questions and ten answers about stem cells, and I will learn about her magic with you.
Through ten groups of questions and answers, this paper gives you the function and application of popular science stem cells, and shows you the important position of stem cell therapy in modern medical care.

Mother, the pilot of the boat of life, not only gave birth to us, but also promoted the reproduction of mankind. She is a great inheritor of life and a transmitter of love.
Cells, the weavers of the web of life, constitute the cornerstone of the human body, which is a miracle exhibitor with various forms and complicated functions.
The human body is a magnificent movement interwoven with countless cells, the harmonious resonance of 240 kinds and 60 trillion cells, and the subtle fusion of 4 major organizations, 36 organs and 8 major systems.
She is a special cell, but also the guardian of the source of life. She can regenerate new cells, replace aging cells and repair damaged tissues and organs. She is the mother of the cell world.
This kind of cell is the root of our life-stem cells.
With the progress of science, stem cell research has become one of the most advanced and active research directions in the global medical field.
However, for the general public, what exactly are stem cells? What does it do? What kind of people are suitable for repair intervention through stem cells? What are the risks even in treatment? This article will help you understand these questions easily through ten groups of questions and answers.
Ten questions and answers about stem cells
01
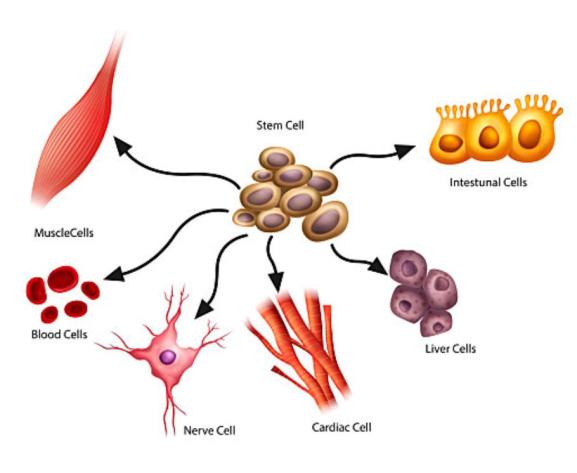
What are stem cells?
Stem cells are cells with self-renewal function and multi-directional differentiation ability.
Under certain conditions, these cells can differentiate into more than 220 different functional cells in human body. Because of its remarkable homing effect, stem cells can repair and replace damaged cells and promote organ regeneration. They are the basic cells that constitute various tissues and organs of the human body, so they are known as "the source of life" and are often called "universal cells" in the medical field.
02
What are the classifications of stem cells?
Scientific research shows that stem cells exist not only in embryos, but also in adults, which can be extracted from cord blood, umbilical cord, placenta, bone marrow, fat and other tissues.
Stem cells are divided into totipotent stem cells, pluripotent stem cells and unipotent stem cells according to their extensive differentiation ability.
Stem cells can be divided into embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells according to their stages of embryonic development.
According to the tissue type of stem cell differentiation, it can be divided into hematopoietic stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells.
03
What is stem cell therapy?
"Stem cell therapy" refers to a medical intervention that extracts stem cells from patients or uses other stem cells, cultivates them under laboratory conditions, and then transfuses them into patients through specific transplantation techniques, so as to repair the cells and tissues that have lost their functions, thus promoting their regeneration and improving their symptoms. At present, hematopoietic stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells are widely used in clinic.
04
What is the difference between autologous and allogeneic stem cells?
Autologous stem cells are derived from patients themselves, which have perfect tissue compatibility, no need for matching, high utilization rate of transplanted cells and no rejection.
Allogeneic stem cells are derived from individuals other than patients and have low immunogenicity. Autologous stem cells are not recommended for people with infectious diseases, major genetic diseases or other health problems.
05
How can stem cells be used to treat diseases?
Cells are the basic unit of life. Human life is accompanied by the process of self-replication and differentiation of stem cells from birth to growth. The ability of stem cells to treat diseases mainly stems from their biological characteristics, which include:
The ability of long-term survival and continuous self-replication;
It can differentiate across different lines and germ layers, showing high plasticity;
And its chemical tendency, that is, homing effect, provides an important biological basis for cell therapy.
06
Is stem cell therapy risky?
Compared with conventional drug therapy, stem cell therapy is considered safer and has fewer side effects. But this does not mean that the risk is zero. Looking at stem cell therapy objectively, the following are some main risks of stem cell therapy:
Tumor development: If stem cells divide or differentiate into abnormal cells uncontrollably, it may lead to cancer. This mainly applies to embryonic or fetal stem cells, or reprogrammed stem cells, because the risk is based on their pluripotency.
Immune rejection: The body may regard foreign stem cells as a threat and attack them, leading to inflammation and injury. This is more likely to happen in hematopoietic stem cells (HSC).
Infection or complications related to invasive medical procedures: Stem cell therapy may lead to infection or complications related to invasive medical procedures.
Drug interaction: Stem cell therapy may have unpredictable interactions with other drugs taken by patients, which may lead to adverse drug interactions.
Unconfirmed or untested stem cell therapy: There is also the risk that unscrupulous practitioners provide unconfirmed or untested stem cell therapy, which may be unsafe or effective.
The effect of treatment is uncertain: patients should also realize that stem cell therapy does not guarantee a cure, and in some cases, it may not be effective at all. Stem cell therapy may not provide lasting results, and patients may need additional treatment.
It should be noted that these risks may be different due to individual differences, treatment methods, stem cell types and other factors. Before receiving stem cell therapy, patients should fully discuss these risks with doctors and weigh the potential benefits and risks of treatment.
07
What diseases can stem cell therapy treat?
Stem cell therapy is mainly used in the fields of treatment, health care and beauty, and it is also used to improve some refractory diseases.
Heart disease: Stem cells can regenerate damaged heart cells and maintain the health and vitality of the heart through a specific process of induced differentiation in the treatment of heart disease.
Prevention and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: Injecting induced differentiated stem cells can replace aging brain cells and improve cognitive function.
Treatment of liver cirrhosis: generate liver cells through differentiation, and promote the regeneration and repair of liver cells.
Cancer treatment: Directionally differentiated stem cells can enhance the body’s immune function and help fight tumors.
Treatment of premature ovarian failure: Stem cell therapy can restore ovarian function, promote the repair of damaged tissues, improve ovarian microenvironment, enhance reproductive capacity, prevent follicular atresia and promote follicular renewal.
Male hypofunction: Stem cell therapy can repair the aging of reproductive system, improve sexual function, maintain the balance of sex hormones, reduce nocturia, relieve the symptoms of prostatic hyperplasia, and help prevent prostate hypertrophy and other problems.
Enhance muscle function: with the increase of age, muscle function weakens, strength and relaxation function decline, and the body is bloated. Stem cell therapy can improve muscle function, enhance strength, improve body shape and show youthfulness.
08
What is the effect of stem cell therapy?
Stem cell therapy can be carried out by systemic infusion or fixed-point intervention. Clinicians adopt appropriate cell types and treatment strategies according to patients’ health status and disease needs.
Because this treatment can directly intervene in the cause of disease, avoid other physical injuries that may be caused by drugs and surgery, and help regulate the sub-health state, the effect is usually not limited to treating diseases, but also improving the overall function.
09
Is there an age limit for stem cell transfusion?
Traditionally, some types of stem cell transplantation, such as allogeneic bone marrow transplantation, often have age restrictions, and it is usually recommended to be 50 years old or under 45 years old. However, with the progress of medical technology, this limitation is being broken.
For example, it has been reported that a 71-year-old patient successfully received autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, and a 69-year-old woman also successfully received her son’s hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
These cases show that under proper medical conditions and monitoring, elderly patients may also successfully receive stem cell transfusion therapy, which proves that the age limit is gradually relaxing.
10
What are the taboo populations of stem cells?
Patients with advanced malignant brain tumors, especially brain tumors;
Patients with shock or general failure with abnormal vital signs (requiring disease correction) and those who do not cooperate with the examination;
Patients with heart, lung, liver, kidney and other important organ dysfunction (multiple organ dysfunction syndrome);
Patients with dysfunction of coagulation mechanism;
Patients with severe local infection;
Patients with positive serological results (such as HIV, hepatitis B, syphilis, etc.);
People with high allergic constitution or severe allergic history;
People with nervous system diseases or diseases that have not been diagnosed;
This group is in a special situation and has uncontrollable risks, so it needs careful diagnosis and treatment.
Write it at the end
Stem cells have excellent regeneration and repair functions, and these abilities will gradually weaken with age. Therefore, it is an increasingly popular choice to store healthy stem cells as early as possible, which will provide the possibility for future health management and disease treatment.
The 21st century will be the era of cell therapy, and the application of stem cells and immune cells is expected to play an important role in clinical treatment.
However, at present, except for the mature clinical application of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, other types of stem cell therapy are mostly in the research stage, and strictly designed clinical trials are needed to prove their clinical advantages, safety and effectiveness, which need further study.
Moreover, non-compliant and eager stem cell therapy and research not only threaten the safety of patients, but also hinder the improvement of stem cell therapy and its research level, which needs the attention of legal supervision, and patients with hope in stem cell therapy should also be alert to fraud and pay attention to its development and related policies and regulations.
Original title: "Why do you call her" the mother of cells ":Ten questions and ten answers about stem cells, and learn about her magic with you"
Read the original text